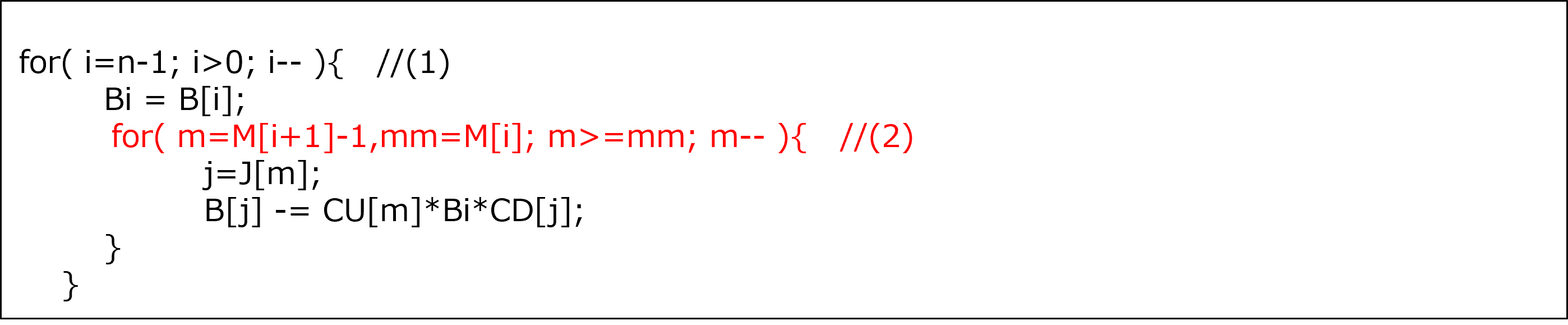4.4. Changing the access direction of arrays¶
4.4.1. Target for this tuning¶
The target for tuning in this section is the function “othSolv_function_3”, which is in the measurement region “Processing the equations other than system of equations”. In the initial version of the Application, the cost of this function was 0.8% of that of the entire Application.
4.4.2. Analysis¶
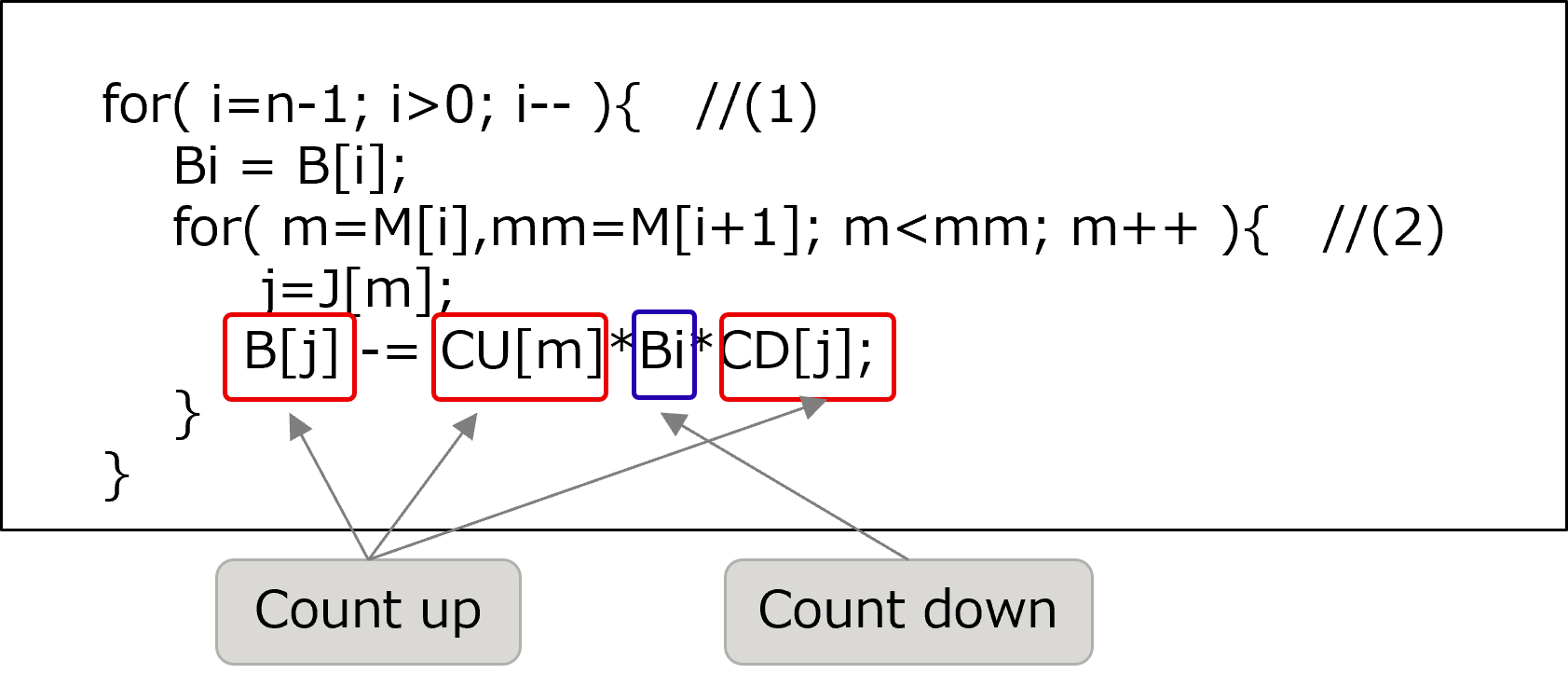
The following nested loop was selected as a target after the analysis of the function “othSolv_function_3”. The key points of this source code are as follows:
In the source code, the counter variable “i” in the loop (1) was decreased by 1. On the other hand, the counter variable “m” in the loop (2) was increased by 1.
Therefore, the access direction was different between the array “Bi” and the arrays “B”, ”CU”, and “CD”. Hence cache misses may have occurred frequently.
[Some lines from function “othSolv_function_3” before this tuning was performed]
4.4.3. Tuning¶
The following tuning was performed.
In order to reduce the number of cache misses, the loop (2) was changed to the counting down loop as well as the loop (1).
[Some lines from function “othSolv_function_3” after this tuning was performed]
4.4.4. Evaluation of the performance¶
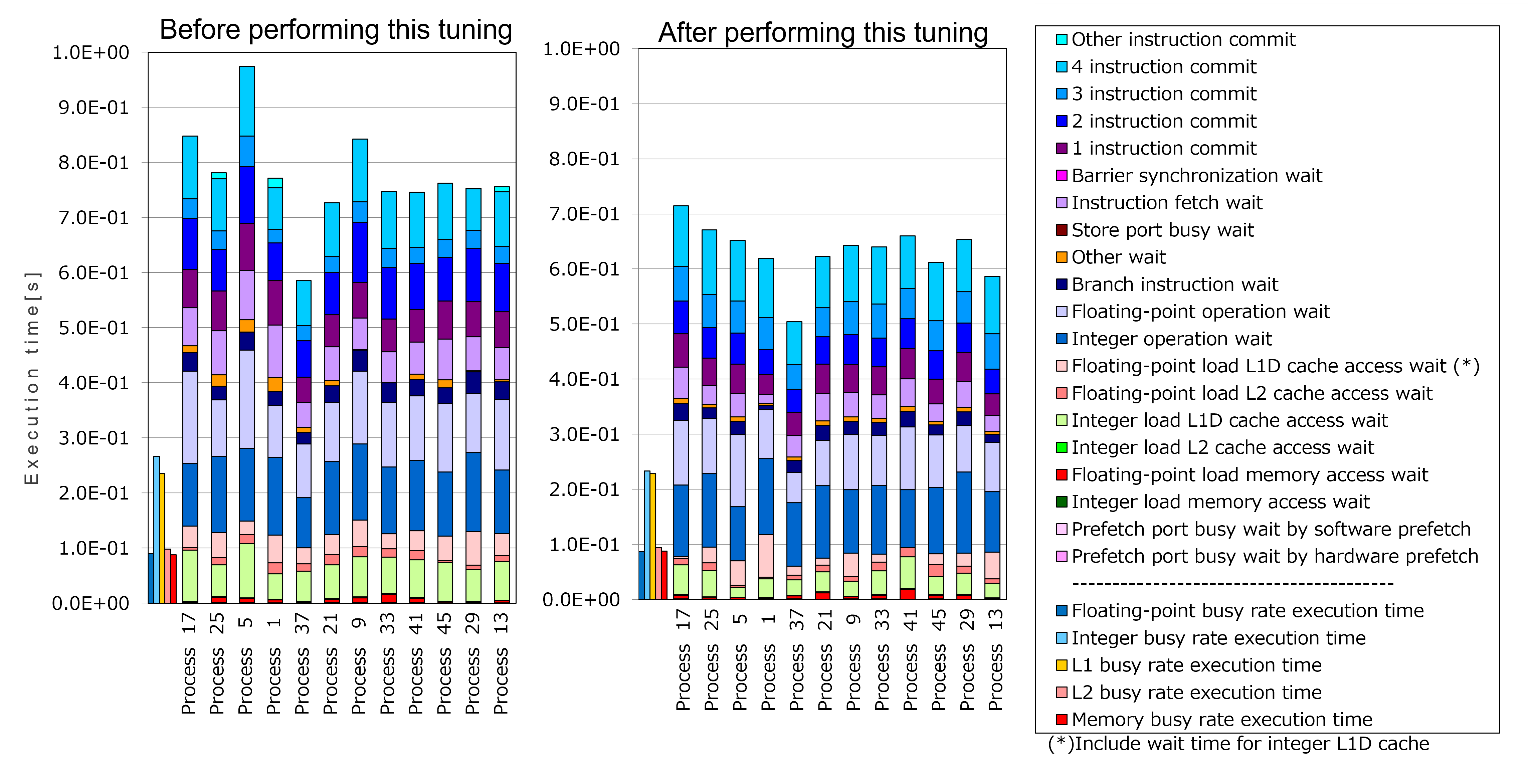
To evaluate the effect of this tuning, “cycle accounting” (output by fapp) in the loop (1) before performing this tuning was compared with that after performing this tuning.
This graph shows “cycle accounting” for 12 processes allocated to one CMG, in the order of their allocation. Each compute node has four CMGs. Each process is allocated to each CMG in order, so the process numbers in the graph are incremented by four.
As seen in the graphs above, the execution time measured before performing this tuning (depends on the longest process, Process 5) was 0.97 seconds. On the other hand, the execution time measured after performing this tuning (similarly, Process 17) was 0.71 seconds. This means about 27% improvement.
Especially, the execution time of “Integer load L1D cache access wait” and “Instruction fetch wait” was significantly improved by this tuning. This improvement indicates the effect of the hardware prefetch.
Finally, “Floating-point operation wait” was also improved. This indicates the improvement of the instruction scheduling.